AWS側は、マネージドVPNサービスのSite to Site VPNを使う。
オンプレミス側は、ソフトウェアルータのvyosのvpnサービスを使う。
AWS側の構築
適当なvpcを作り、カスタマーゲートウェイ、仮装プライベートゲートウェイ、Site to Site VPNを作る。
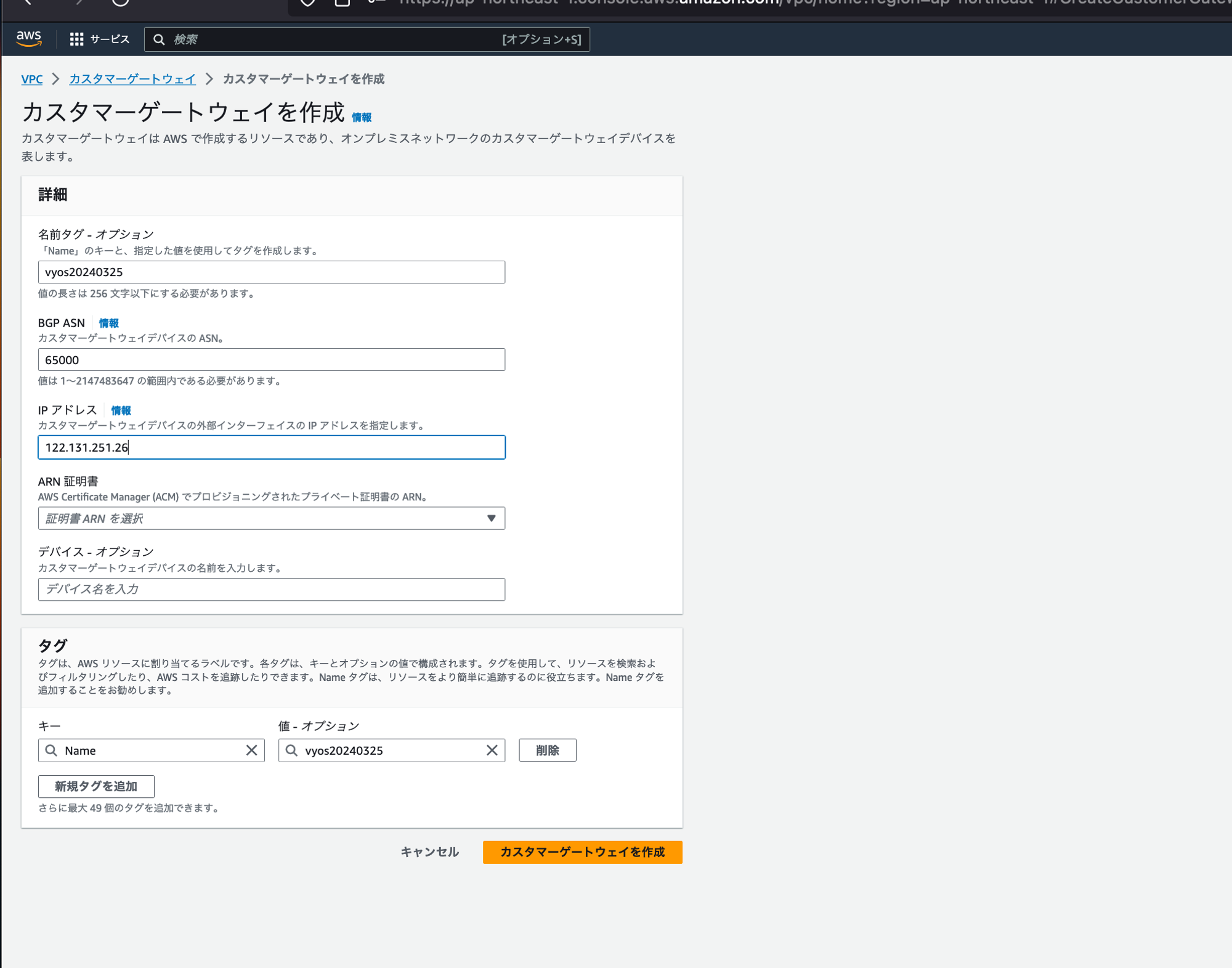
カスタマーゲートウェイを作る。
IPアドレスは、オンプレミス側のグローバルIPを指定する。
ポートの穴あけができない場合、NATされている場合でも同じように指定する。
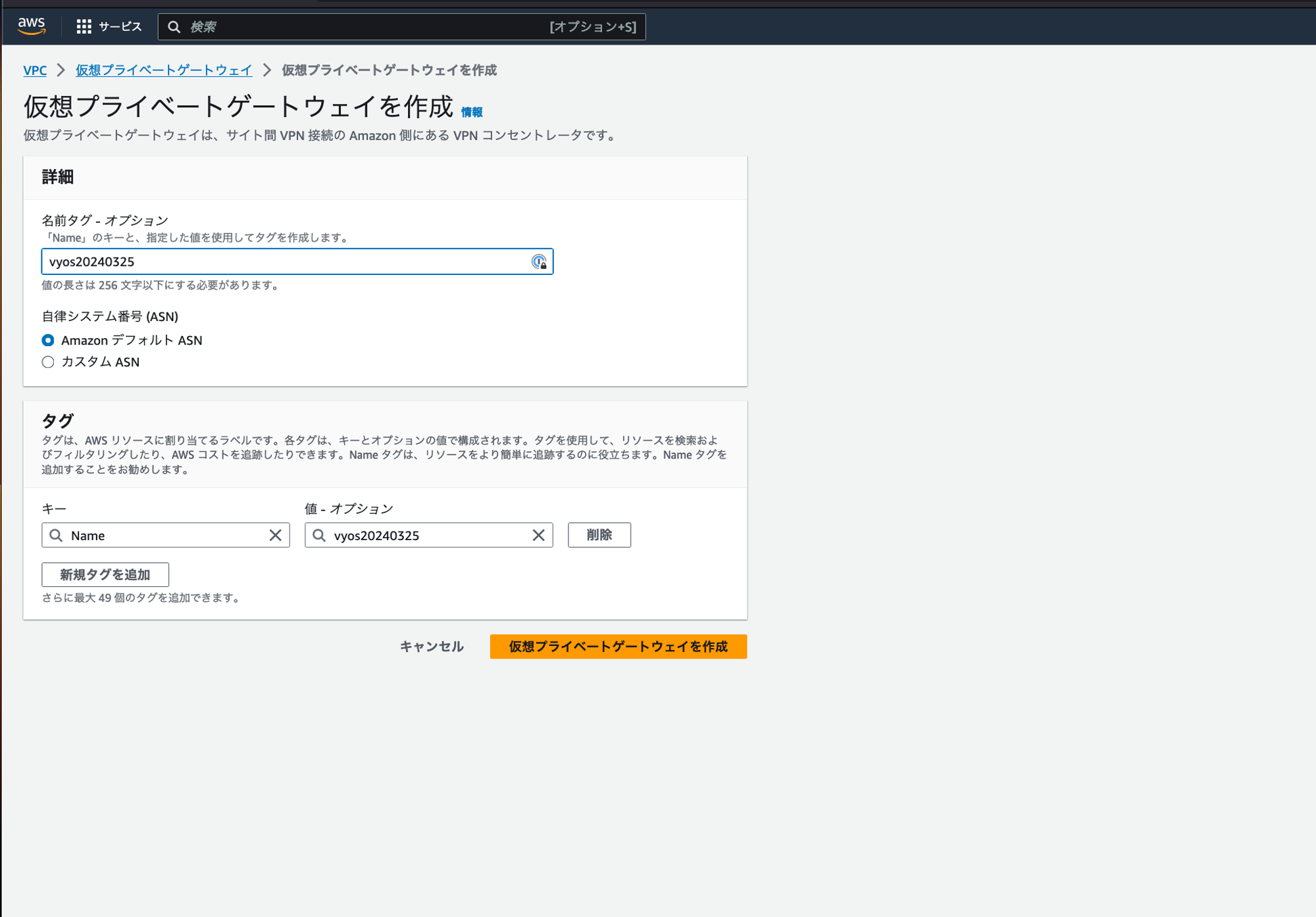
仮装プライベートゲートウェイを作る。
AWS側のASNとなり、基本的にデフォルトで良い。
用意したいASNがAWS側と被るのであれば変える必要があるはず。
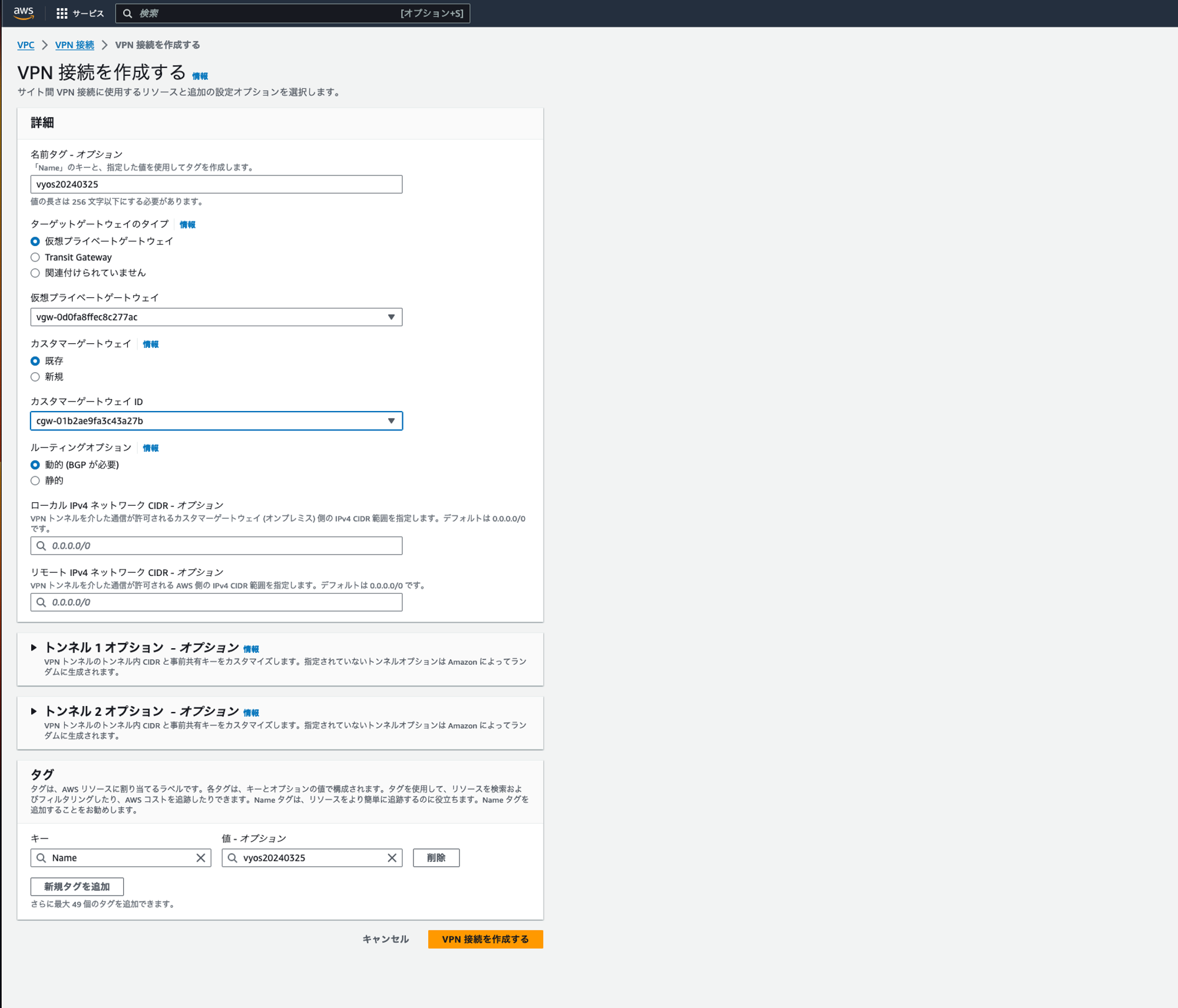
Site To Site VPNを作る。
上記で作成したカスタマーゲートウェイと仮装プライベートゲートウェイを指定するのみで良い。
vyosではBGPを扱うことができるため、せっかくなのでBGPを使いたいので、有効にしておく。
このような形で作られる。
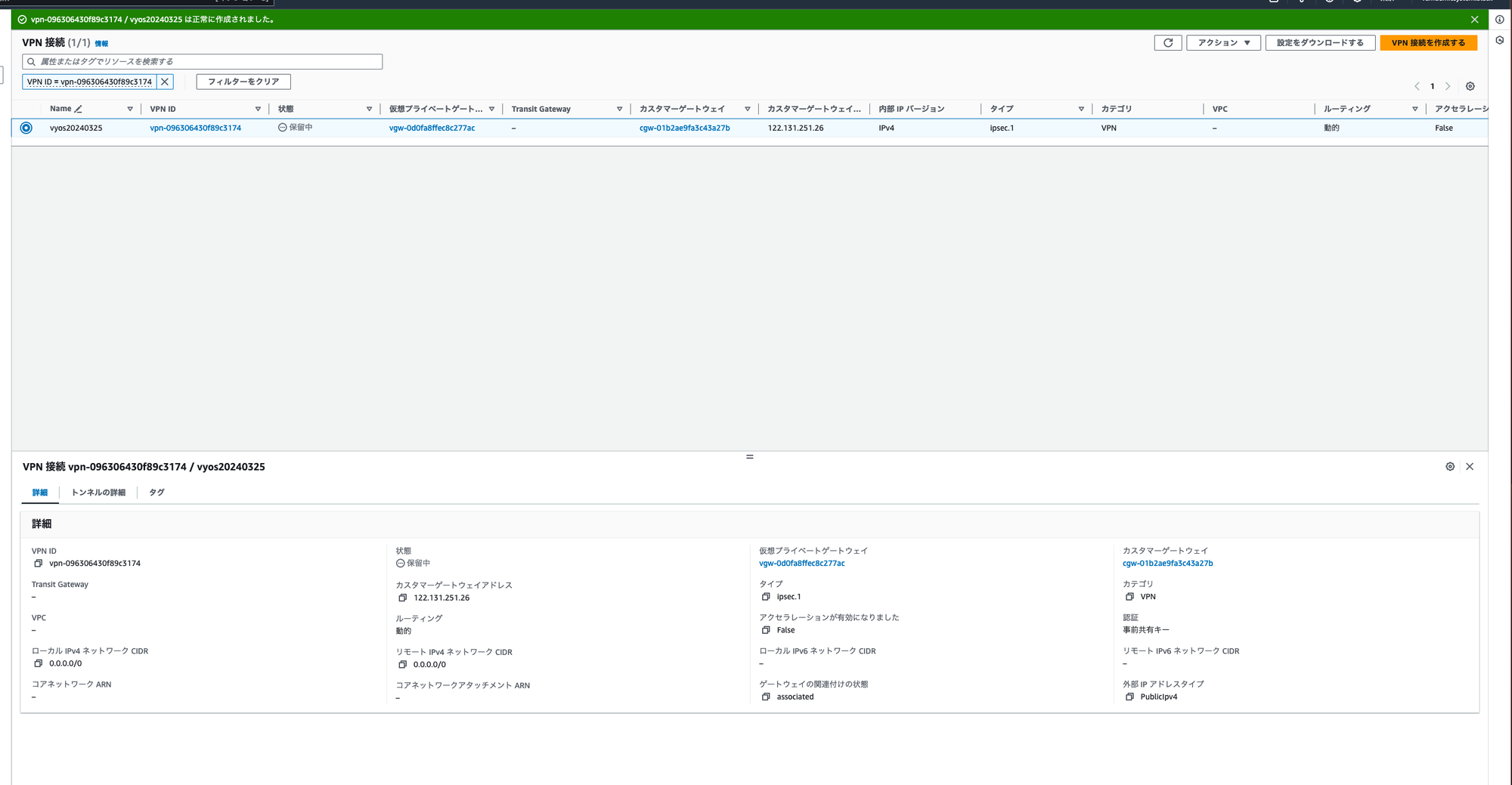
オンプレミス側の構築
構築するvyosは2つNICかあり、eth0はNATルータと同じネットワーク、eth1はvyosからのみ接続されているプライベートネットワークの想定。
大きく2つのフローがあり、まずはipsecvpnトンネリングの確立が必要。その後にbgpの設定を入れていく。
慣れていればいいのだけど、一緒にやると切り分けが面倒くさいので、1つづつやっていく。
ちなみに、本来であれば、冗長性を持たすために2系統のトンネリング接続を設定することが推奨されているが、検証なので1系統のみやる。2系統やる時は必要な設定を単純に置き換えれば接続はできるはず。
基本設定
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 192.168.50.106/24 set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 172.16.2.1/24 set protocols static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 192.168.50.1 set service ssh
AWS側でルータ側に設定するConfigサンプルをダウンロードできるので、それをvyos用コマンドに変換していく。
set interfaces vti vti0 address '169.254.177.182/30' set interfaces vti vti0 description 'VPC tunnel 1' set interfaces vti vti0 mtu '1436' # set vpn ipsec esp-group AWS compression set vpn ipsec esp-group AWS lifetime '3600' set vpn ipsec esp-group AWS mode 'tunnel' set vpn ipsec esp-group AWS pfs 'enable' set vpn ipsec esp-group AWS proposal 1 encryption 'aes128' set vpn ipsec esp-group AWS proposal 1 hash 'sha1' set vpn ipsec ike-group AWS dead-peer-detection action 'restart' set vpn ipsec ike-group AWS dead-peer-detection interval '15' set vpn ipsec ike-group AWS dead-peer-detection timeout '30' set vpn ipsec ike-group AWS lifetime '28800' set vpn ipsec ike-group AWS proposal 1 dh-group '2' set vpn ipsec ike-group AWS proposal 1 encryption 'aes128' set vpn ipsec ike-group AWS proposal 1 hash 'sha1' # インターネットに接続しているルータがNATしている場合はこちらの設定を入れる ここから---- set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 authentication local-id 122.131.251.26 set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 authentication remote-id 13.230.113.189 set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 local-address 192.168.50.106 # ここまで---- set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 remote-address 13.230.113.189 set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 authentication mode 'pre-shared-secret' set vpn ipsec authentication psk vyos id 13.230.113.189 set vpn ipsec authentication psk vyos secret '1hNvlDTZTXqfDh5PUaVSL7BrTshHk.Q3' set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 description 'VPC tunnel 1' set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 ike-group 'AWS' set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 vti bind 'vti0' set vpn ipsec site-to-site peer 13-230-113-189 vti esp-group 'AWS' # commitしたときに警告が出る set vpn ipsec option disable-route-autoinstall commit save exit # デバッグする時 show log vpn
接続状態を確認する。
接続成功していれば、それぞれstateがupとなっているはず。
vyos@vyos:~$ show vpn ike sa
Peer ID / IP Local ID / IP
------------ -------------
13.230.113.189 13.230.113.189 192.168.50.106 192.168.50.106
State IKEVer Encrypt Hash D-H Group NAT-T A-Time L-Time
----- ------ ------- ---- --------- ----- ------ ------
up IKEv2 AES_CBC_128 HMAC_SHA1_96 MODP_1024 yes 167 28031
vyos@vyos:~$ show vpn ipsec sa Connection State Uptime Bytes In/Out Packets In/Out Remote address Remote ID Proposal ------------------ ------- -------- -------------- ---------------- ---------------- -------------- ------------------------ 13-230-113-189-vti up 3m9s 120B/80B 2/2 13.230.113.189 13.230.113.189 AES_CBC_128/HMAC_SHA1_96
また、AWS側の状態もステータスが「アップ」となる。
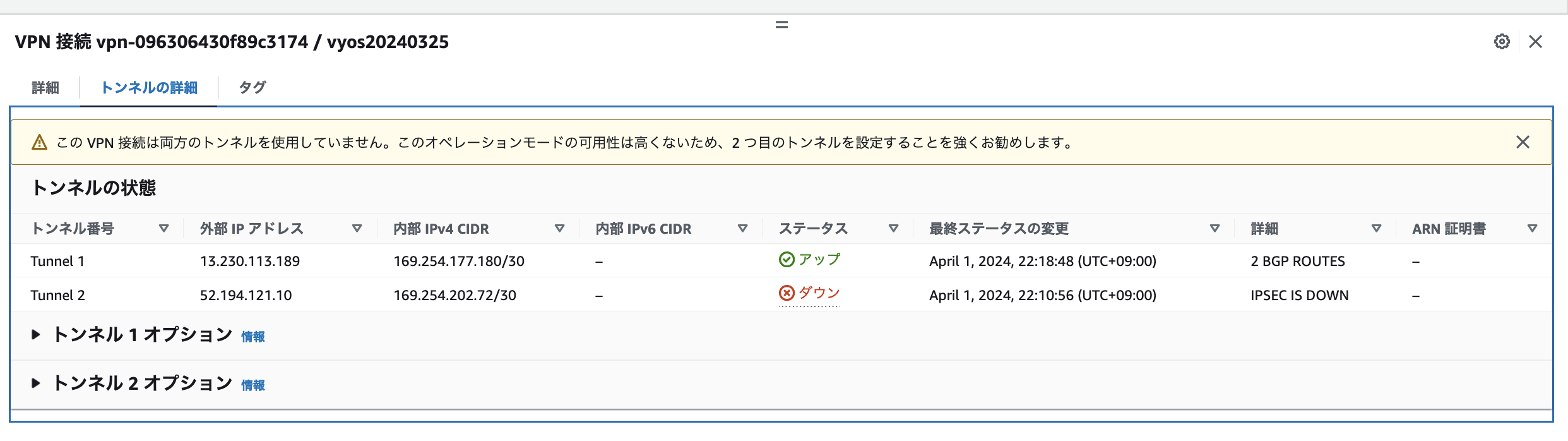
AWS側のVPNの内部IPへの接続性を確認する。ネットワークアドレスが、169.254.177.180/30なので、169.254.177.181と169.254.177.182の2つしかない。
ダウンロードしたConfigを見ると、このようになっているので、181がVPN側、182がオンプレミス側。ということになる。
Inside IP Addresses - Customer Gateway : 169.254.177.182/30 - Virtual Private Gateway : 169.254.177.181/30
vyos@vyos:~$ ping 169.254.177.181 count 3 PING 169.254.177.181 (169.254.177.181) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 169.254.177.181: icmp_seq=1 ttl=254 time=5.29 ms 64 bytes from 169.254.177.181: icmp_seq=2 ttl=254 time=5.54 ms 64 bytes from 169.254.177.181: icmp_seq=3 ttl=254 time=5.35 ms --- 169.254.177.181 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 5.286/5.391/5.544/0.110 ms
続いて、bgpの設定をする。
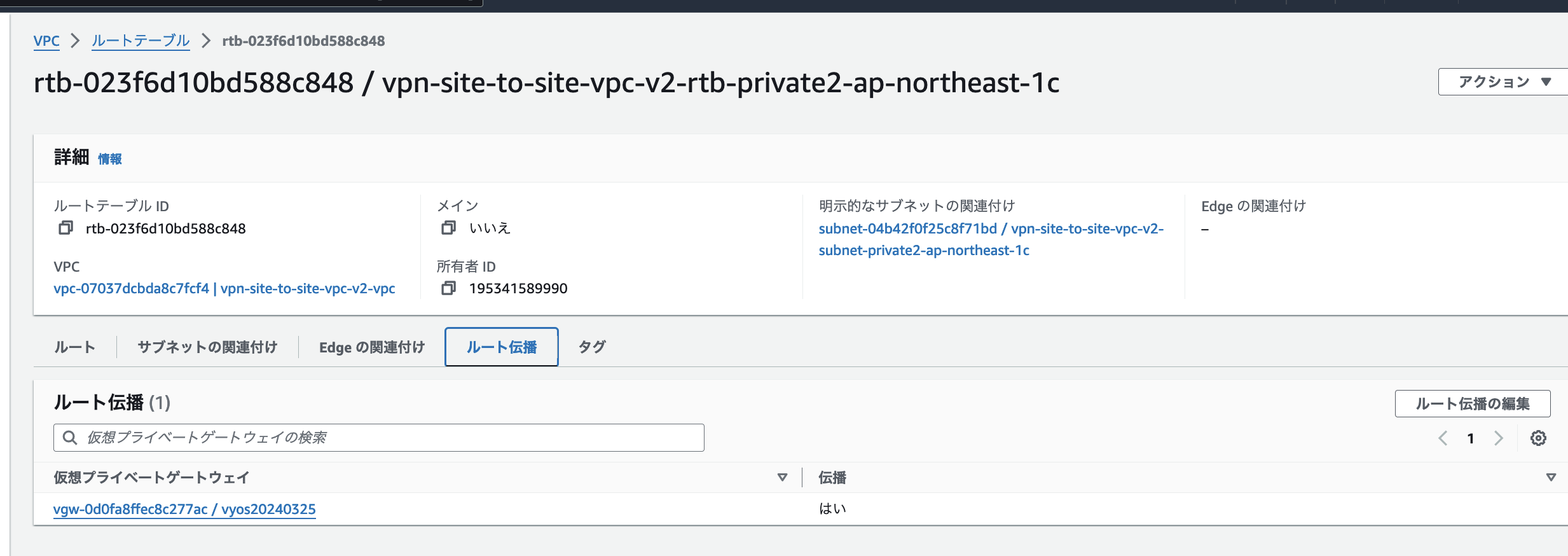
AWS側で仮想プライベートゲートウェイへのルート伝播を有効にしておく。
一般的には、経路宣伝という言葉が、AWSだとルート伝播という言葉のよう。
これを設定することで、対抗のルータがBGPに対応していれば、ルーティングを渡すことできる。(厳密にはコピーしているはず)
# vyos側 set protocols bgp system-as 65000 set protocols bgp neighbor 169.254.177.181 remote-as '64512' set protocols bgp neighbor 169.254.177.181 address-family ipv4-unicast soft-reconfiguration inbound set protocols bgp neighbor 169.254.177.181 update-source '192.168.50.106' set protocols bgp timers holdtime '30' set protocols bgp timers keepalive '10' # 経路宣伝 set protocols bgp address-family ipv4-unicast network 192.168.50.0/24 set protocols bgp address-family ipv4-unicast network 172.16.2.0/24 # 保存 commit save exit restart all
設定後、bgp設定が反映されているか確認する。
vyos@vyos:~$ show ip bgp summary IPv4 Unicast Summary (VRF default): BGP router identifier 192.168.50.106, local AS number 65000 vrf-id 0 BGP table version 2 RIB entries 3, using 288 bytes of memory Peers 1, using 20 KiB of memory Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc 169.254.177.181 4 64512 12447 12447 2 0 0 1d10h33m 1 2 N/A Total number of neighbors 1
オンプレミス側から見たネイバー169.254.177.181の設定。つまるところ、VPN側の設定を参照できる。
ルーティングテーブルを見てみると、オンプレミス側の192.168.50.0のルーティングが伝播していることがわかる。
vyos@vyos:~$ show ip bgp neighbors 169.254.177.181 routes
BGP table version is 2, local router ID is 192.168.50.106, vrf id 0
Default local pref 100, local AS 65000
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, = multipath,
i internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed
Nexthop codes: @NNN nexthop's vrf id, < announce-nh-self
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.0.0.0/16 169.254.177.181 100 0 64512 i
Displayed 1 routes and 2 total paths
vyos@vyos:~$ show ip bgp neighbors 169.254.177.181 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 2, local router ID is 192.168.50.106, vrf id 0
Default local pref 100, local AS 65000
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, = multipath,
i internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed
Nexthop codes: @NNN nexthop's vrf id, < announce-nh-self
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.0.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 0 64512 i
*> 192.168.50.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 2
vyos側のルートテーブルをみると、10.0.0.0/16のルーティングがBGPにより伝播していることがわかる。
vyos@vyos:~$ show ip route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP,
O - OSPF, I - IS-IS, B - BGP, E - EIGRP, N - NHRP,
T - Table, v - VNC, V - VNC-Direct, A - Babel, F - PBR,
f - OpenFabric,
> - selected route, * - FIB route, q - queued, r - rejected, b - backup
t - trapped, o - offload failure
S>* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.50.1, eth0, weight 1, 1d11h09m
B>* 10.0.0.0/16 [20/100] via 169.254.177.181, vti0, weight 1, 1d11h00m
C>* 169.254.177.180/30 is directly connected, vti0, 1d11h10m
C>* 172.16.2.0/24 is directly connected, eth1, 1d11h10m
C>* 192.168.50.0/24 is directly connected, eth0, 1d11h10m
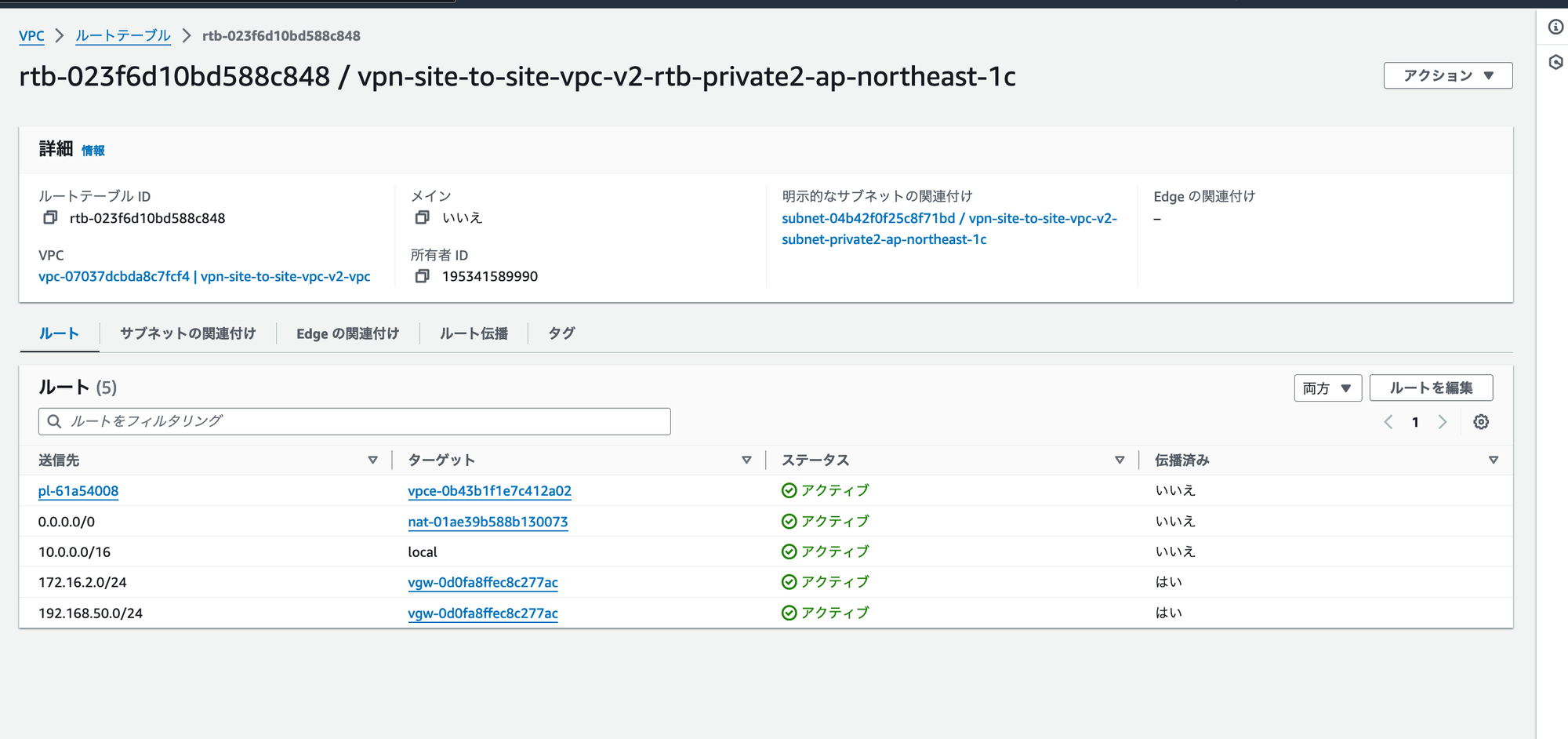
AWS側のルートテーブルを直接みると、このようになっている。
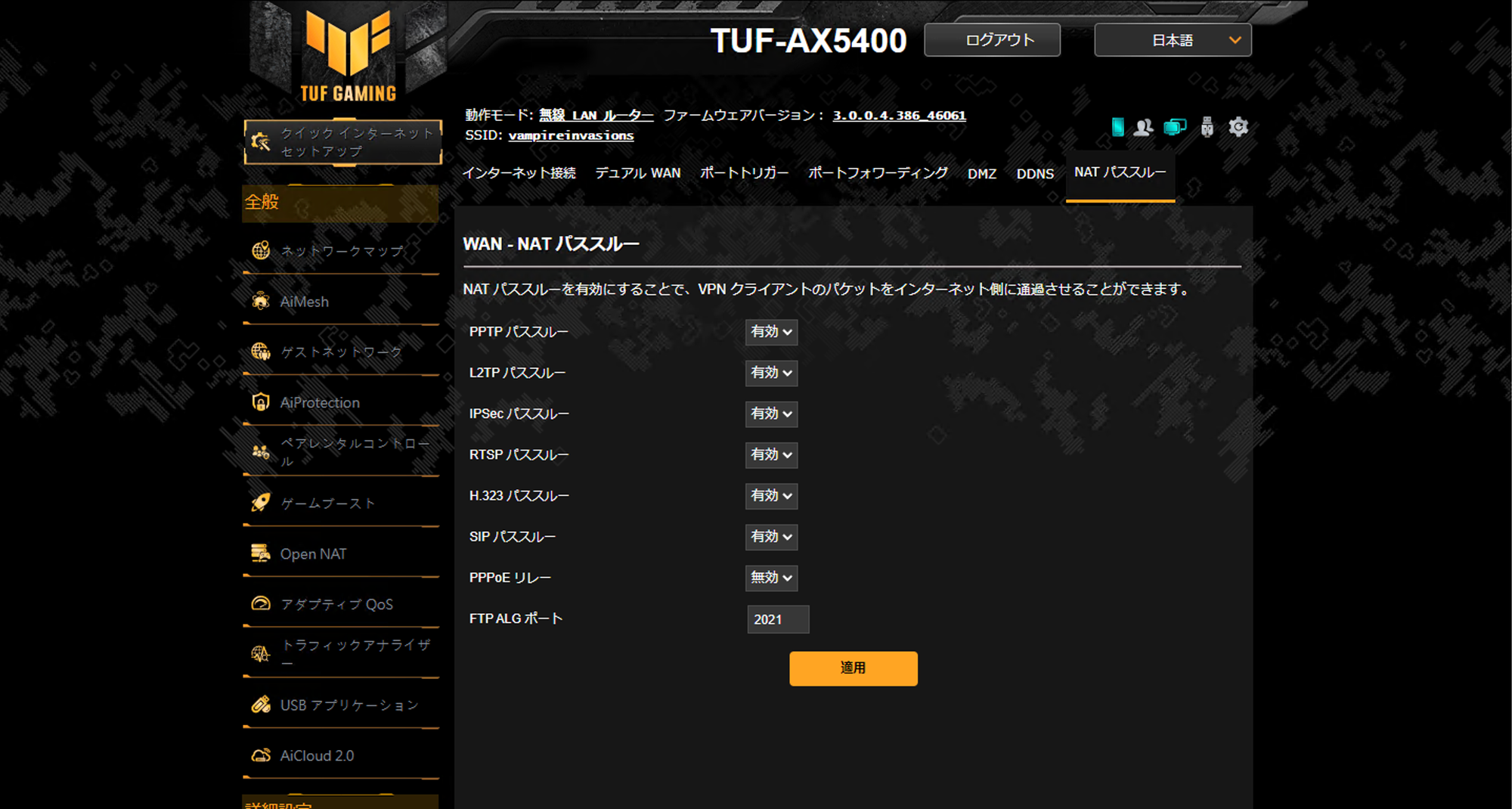
NATルータの場合は、ルータの設定も一応確認しておく。
確認したいポイントは、このルータの場合は、IPSecパススルーが有効になっているかどうか。
もうちょっと具体的な設定ができる場合は、ポート4500と500が、オンプレミス側のVPNルータのIP(今回の場合、192.168.50.106)へのNATトラバーサル設定が入っているかどうか。
動作確認
vpc内に、適当なEC2を作る。
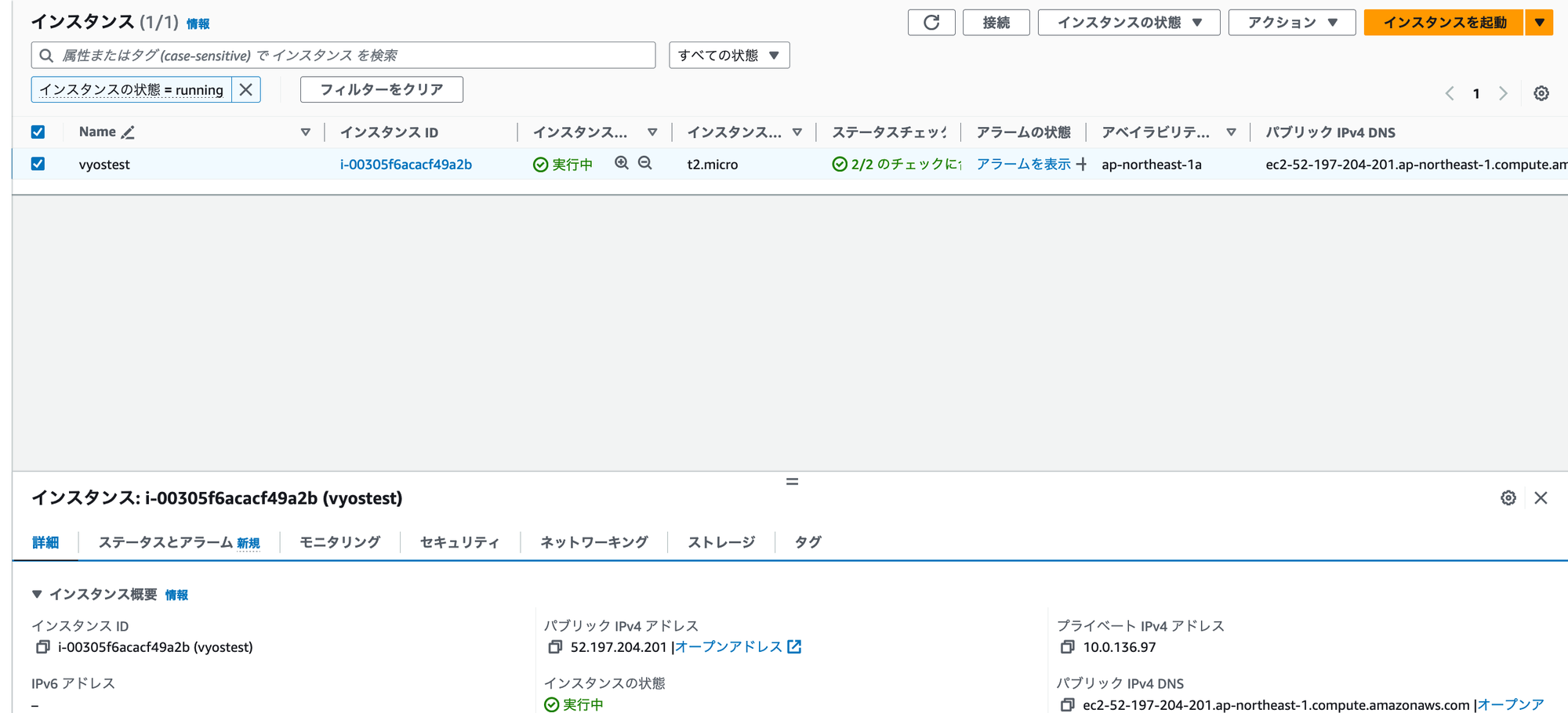
vpnルータ配下の適当なマシンから、EC2にpingを送って接続できればOK。
ちなみに、vpnルータと化しているvyosからpingを送っても到達しなかった。
pingを送る際に、interfaceを指定できるのだけど、指定してもダメだった。
vyos@vyos:~$ ping 10.0.136.97 count 3 PING 10.0.136.97 (10.0.136.97) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.136.97: icmp_seq=1 ttl=126 time=7.12 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.136.97: icmp_seq=2 ttl=126 time=6.80 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.136.97: icmp_seq=3 ttl=126 time=7.79 ms --- 10.0.136.97 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 6.798/7.235/7.790/0.413 ms vyos@vyos:~$
AWSからダウンロードしたConfig
Amazon Web Services
Virtual Private Cloud
VPN Connection Configuration
================================================================================
AWS utilizes unique identifiers to manipulate the configuration of
a VPN Connection. Each VPN Connection is assigned a VPN Connection Identifier
and is associated with two other identifiers, namely the
Customer Gateway Identifier and the Virtual Private Gateway Identifier.
Your VPN Connection ID : vpn-096306430f89c3174
Your Virtual Private Gateway ID : vgw-0d0fa8ffec8c277ac
Your Customer Gateway ID : cgw-01b2ae9fa3c43a27b
A VPN Connection consists of a pair of IPSec tunnel security associations (SAs).
It is important that both tunnel security associations be configured.
IPSec Tunnel #1
================================================================================
#1: Internet Key Exchange Configuration
Configure the IKE SA as follows:
Please note, these sample configurations are for the minimum requirement of AES128, SHA1, and DH Group 2.
Category "VPN" connections in the GovCloud region have a minimum requirement of AES128, SHA2, and DH Group 14.
You will need to modify these sample configuration files to take advantage of AES256, SHA256, or other DH groups like 2, 14-18, 22, 23, and 24.
NOTE: If you customized tunnel options when creating or modifying your VPN connection, you may need to modify these sample configurations to match the custom settings for your tunnels.
Higher parameters are only available for VPNs of category "VPN," and not for "VPN-Classic".
The address of the external interface for your customer gateway must be a static address.
Your customer gateway may reside behind a device performing network address translation (NAT).
To ensure that NAT traversal (NAT-T) can function, you must adjust your firewall !rules to unblock UDP port 4500.
If not behind NAT, and you are not using an Accelerated VPN, we recommend disabling NAT-T. If you are using an Accelerated VPN, make sure that NAT-T is enabled.
- IKE version : IKEv2
- Authentication Method : Pre-Shared Key
- Pre-Shared Key : 1hNvlDTZTXqfDh5PUaVSL7BrTshHk.Q3
- Authentication Algorithm : sha1
- Encryption Algorithm : aes-128-cbc
- Lifetime : 28800 seconds
- Phase 1 Negotiation Mode : main
- Diffie-Hellman : Group 2
#2: IPSec Configuration
Configure the IPSec SA as follows:
Category "VPN" connections in the GovCloud region have a minimum requirement of AES128, SHA2, and DH Group 14.
Please note, you may use these additionally supported IPSec parameters for encryption like AES256 and other DH groups like 2, 5, 14-18, 22, 23, and 24.
NOTE: If you customized tunnel options when creating or modifying your VPN connection, you may need to modify these sample configurations to match the custom settings for your tunnels.
Higher parameters are only available for VPNs of category "VPN," and not for "VPN-Classic".
- Protocol : esp
- Authentication Algorithm : hmac-sha1-96
- Encryption Algorithm : aes-128-cbc
- Lifetime : 3600 seconds
- Mode : tunnel
- Perfect Forward Secrecy : Diffie-Hellman Group 2
IPSec Dead Peer Detection (DPD) will be enabled on the AWS Endpoint. We
recommend configuring DPD on your endpoint as follows:
- DPD Interval : 10
- DPD Retries : 3
IPSec ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) inserts additional
headers to transmit packets. These headers require additional space,
which reduces the amount of space available to transmit application data.
To limit the impact of this behavior, we recommend the following
configuration on your Customer Gateway:
- TCP MSS Adjustment : 1379 bytes
- Clear Don't Fragment Bit : enabled
- Fragmentation : Before encryption
#3: Tunnel Interface Configuration
Your Customer Gateway must be configured with a tunnel interface that is
associated with the IPSec tunnel. All traffic transmitted to the tunnel
interface is encrypted and transmitted to the Virtual Private Gateway.
The Customer Gateway and Virtual Private Gateway each have two addresses that relate
to this IPSec tunnel. Each contains an outside address, upon which encrypted
traffic is exchanged. Each also contain an inside address associated with
the tunnel interface.
The Customer Gateway outside IP address was provided when the Customer Gateway
was created. Changing the IP address requires the creation of a new
Customer Gateway.
The Customer Gateway inside IP address should be configured on your tunnel
interface.
Outside IP Addresses:
- Customer Gateway : 122.131.251.26
- Virtual Private Gateway : 13.230.113.189
Inside IP Addresses
- Customer Gateway : 169.254.177.182/30
- Virtual Private Gateway : 169.254.177.181/30
Configure your tunnel to fragment at the optimal size:
- Tunnel interface MTU : 1436 bytes
#4: Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Configuration:
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGPv4) is used within the tunnel, between the inside
IP addresses, to exchange routes from the VPC to your home network. Each
BGP router has an Autonomous System Number (ASN). Your ASN was provided
to AWS when the Customer Gateway was created.
BGP Configuration Options:
- Customer Gateway ASN : 65000
- Virtual Private Gateway ASN : 64512
- Neighbor IP Address : 169.254.177.181
- Neighbor Hold Time : 30
Configure BGP to announce routes to the Virtual Private Gateway. The gateway
will announce prefixes to your customer gateway based upon the prefix you
assigned to the VPC at creation time.
IPSec Tunnel #2
================================================================================
#1: Internet Key Exchange Configuration
Configure the IKE SA as follows:
Please note, these sample configurations are for the minimum requirement of AES128, SHA1, and DH Group 2.
Category "VPN" connections in the GovCloud region have a minimum requirement of AES128, SHA2, and DH Group 14.
You will need to modify these sample configuration files to take advantage of AES256, SHA256, or other DH groups like 2, 14-18, 22, 23, and 24.
NOTE: If you customized tunnel options when creating or modifying your VPN connection, you may need to modify these sample configurations to match the custom settings for your tunnels.
Higher parameters are only available for VPNs of category "VPN," and not for "VPN-Classic".
The address of the external interface for your customer gateway must be a static address.
Your customer gateway may reside behind a device performing network address translation (NAT).
To ensure that NAT traversal (NAT-T) can function, you must adjust your firewall !rules to unblock UDP port 4500.
If not behind NAT, and you are not using an Accelerated VPN, we recommend disabling NAT-T. If you are using an Accelerated VPN, make sure that NAT-T is enabled.
- IKE version : IKEv2
- Authentication Method : Pre-Shared Key
- Pre-Shared Key : C2agO4BPcD5.8buhLBtSHPX8xgjfJUzG
- Authentication Algorithm : sha1
- Encryption Algorithm : aes-128-cbc
- Lifetime : 28800 seconds
- Phase 1 Negotiation Mode : main
- Diffie-Hellman : Group 2
#2: IPSec Configuration
Configure the IPSec SA as follows:
Category "VPN" connections in the GovCloud region have a minimum requirement of AES128, SHA2, and DH Group 14.
Please note, you may use these additionally supported IPSec parameters for encryption like AES256 and other DH groups like 2, 5, 14-18, 22, 23, and 24.
NOTE: If you customized tunnel options when creating or modifying your VPN connection, you may need to modify these sample configurations to match the custom settings for your tunnels.
Higher parameters are only available for VPNs of category "VPN," and not for "VPN-Classic".
- Protocol : esp
- Authentication Algorithm : hmac-sha1-96
- Encryption Algorithm : aes-128-cbc
- Lifetime : 3600 seconds
- Mode : tunnel
- Perfect Forward Secrecy : Diffie-Hellman Group 2
IPSec Dead Peer Detection (DPD) will be enabled on the AWS Endpoint. We
recommend configuring DPD on your endpoint as follows:
- DPD Interval : 10
- DPD Retries : 3
IPSec ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) inserts additional
headers to transmit packets. These headers require additional space,
which reduces the amount of space available to transmit application data.
To limit the impact of this behavior, we recommend the following
configuration on your Customer Gateway:
- TCP MSS Adjustment : 1379 bytes
- Clear Don't Fragment Bit : enabled
- Fragmentation : Before encryption
#3: Tunnel Interface Configuration
Your Customer Gateway must be configured with a tunnel interface that is
associated with the IPSec tunnel. All traffic transmitted to the tunnel
interface is encrypted and transmitted to the Virtual Private Gateway.
The Customer Gateway and Virtual Private Gateway each have two addresses that relate
to this IPSec tunnel. Each contains an outside address, upon which encrypted
traffic is exchanged. Each also contain an inside address associated with
the tunnel interface.
The Customer Gateway outside IP address was provided when the Customer Gateway
was created. Changing the IP address requires the creation of a new
Customer Gateway.
The Customer Gateway inside IP address should be configured on your tunnel
interface.
Outside IP Addresses:
- Customer Gateway : 122.131.251.26
- Virtual Private Gateway : 52.194.121.10
Inside IP Addresses
- Customer Gateway : 169.254.202.74/30
- Virtual Private Gateway : 169.254.202.73/30
Configure your tunnel to fragment at the optimal size:
- Tunnel interface MTU : 1436 bytes
#4: Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Configuration:
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGPv4) is used within the tunnel, between the inside
IP addresses, to exchange routes from the VPC to your home network. Each
BGP router has an Autonomous System Number (ASN). Your ASN was provided
to AWS when the Customer Gateway was created.
BGP Configuration Options:
- Customer Gateway ASN : 65000
- Virtual Private Gateway ASN : 64512
- Neighbor IP Address : 169.254.202.73
- Neighbor Hold Time : 30
Configure BGP to announce routes to the Virtual Private Gateway. The gateway
will announce prefixes to your customer gateway based upon the prefix you
assigned to the VPC at creation time.
Additional Notes and Questions
================================================================================
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Getting Started Guide:
http://docs.amazonwebservices.com/AmazonVPC/latest/GettingStartedGuide
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Network Administrator Guide:
http://docs.amazonwebservices.com/AmazonVPC/latest/NetworkAdminGuide
参考サイト
https://changineer.info/network/vyatta/vyatta_ipsec_aws.html#google_vignette
https://changineer.info/network/vyatta/vyatta_ipsec_nat.html